Industry
 Num:73
Num:73 See:1872
See:18722021-06
17
How to test the switching power transformer?
Switching power transformer
Switching power transformer is a power transformer that has joined the switching tube. In addition to the voltage conversion function of the ordinary transformer in the circuit, it also has the function of insulation isolation and power transmission. It is generally used in switching power supply and other occasions involving high-frequency circuits.

Function and classification of switching power transformers
The switching power transformer and the switch tube together form a self-excited (or other-excited) type blocking oscillator to convert the input DC voltage into a high frequency pulse voltage.
Play the role of energy transfer and conversion. In a flyback circuit, the transformer converts the electrical energy into a magnetic field that can be stored when the switch is on and released when the switch is off. In a forward circuit, when the switch tube is on, the input voltage is supplied directly to the load and the energy is stored in the inductor. When the switch tube ends, the energy storage inductor continues to transfer to the load.
Classification:
Switching power transformers are divided into single excitation switching power transformers and double excitation switching power transformers. The working principle and structure of the two kinds of switching power transformers are not the same. The input voltage of the single excitation switching power supply transformer is a single polar pulse, and it is also divided into positive and reverse voltage output; The input voltage of the dual-excitation switching power supply transformer is a bipolar pulse, which is generally a bipolar pulse voltage output.
Switching power transformer characteristic parameters
Voltage ratio: The ratio of the primary voltage to the secondary voltage of the transformer.
DC resistance: namely copper resistance.
Efficiency: namely output power/input power *100[%].
Insulation resistance: Insulation ability between the windings of a transformer and between the cores.
Resistance: The extent to which a transformer can withstand a specified voltage within 1 second or 1 minute.
Principle of switching power transformer
For switching power supply, the working principle of switching transformer is different from that of ordinary transformer. Ordinary transformer input AC voltage or current positive and negative half cycle waveform is symmetric, and the input voltage and current waveform is generally continuous, within a period, the average value of the input voltage and current is equal to 0, this is the basic characteristics of the working principle of ordinary transformer; And switch transformer are generally working in switch state, its input voltage or current is generally not sequential, but staccato, the input voltage or current within a period of mean value most of all not equal to zero, therefore, also known as pulse transformer, switch transformer it is a common transformer switch transformer with the biggest difference in terms of working principle.
Through the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control switch tube, the DC voltage after rectification for high frequency switch on, so that the high frequency current into the high frequency transformer primary side of the switching power supply, so that the transformer secondary side to produce inductive current, after rectification you can get the required voltage or multi-channel voltage.
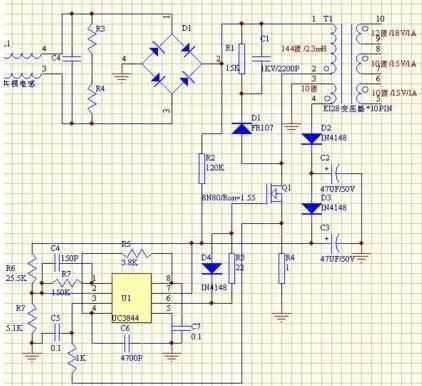
Detecting details of switching power transformers
1, by observing the appearance of the transformer to check whether there is obvious abnormal phenomenon:
For example, whether the coil lead is broken or unsoldered, whether the insulation material has burnt marks, whether the iron core fastening screw is loose, whether the silicon steel sheet is corroded, whether the winding coil is exposed, etc.
2. Insulation test:
Use multimeter R&Times; 10K block respectively measure the core and primary, primary and secondary, core and secondary, electrostatic shielding layer and vent secondary, secondary between the windings of the resistance value, multimeter pointer should refer to the infinite position. Otherwise, the transformer insulation performance is poor.
3, coil on and off detection:
Place the multimeter in R&Times; 1. In the test, if the resistance value of a certain winding is infinite, it indicates that the winding has circuit breakability fault.
4, discrimination of primary and secondary coils:
The primary pin and secondary pin of the power transformer are generally led from both sides respectively, and the primary winding is marked with 220V, the secondary winding is marked with the rated voltage value, such as 15V, 24V, 35V, etc. They are identified by these markers.
5. Detection of no-load current:
A. In the direct measurement method, all the secondary windings are open circuit, and the multimeter is placed in the AC current stop (500mA), and the primary winding is connected in series. When the primary winding plugs into the 220V AC mains, the multimeter indicates the no-load current value.
This value should not be greater than 10% ~ 20% of the transformer's full load current. The normal no-load current of the power transformer for common electronic equipment should be about 100mA. If it exceeds too much, it indicates that the transformer has a short-circuit fault.
B. Indirect measurement method: a 10/5W resistance is connected in series in the primary winding of the transformer, and the secondary is still completely no-load. Turn the multimeter to ac. After the power is added, the voltage drop U at both ends of the resistor R is measured with two meter pens, and then the no-load current I empty is calculated by Ohm's law, that is, I empty =U/R. F? Detection of no-load voltage.
The primary power transformer is connected to 220V mains, and the no-load voltage value of each winding (U21, U22, U23, U24) is measured with a multimeter alternating voltage in turn. The allowable error range is generally: the high-voltage winding ≤±10%, the low-voltage winding ≤±5%, and the voltage difference between the two groups of symmetrical windings with the center tap should be ≤±2%.
6. Test the temperature range of the power transformer:
General small power transformer allowable temperature rise of 40℃ ~ 50℃, if the quality of insulating materials used is good, allowable temperature rise can also be improved.
7. Detect and discriminate the namesake end of each winding:
When using a power transformer, sometimes two or more secondary windings can be connected in series in order to obtain the required secondary voltage. When the power transformer is used in series, the namesake ends of the windings participating in series must be connected correctly and there can be no mistake. Otherwise, the transformer will not work properly.
8. Comprehensive detection and discrimination of short-circuit fault of power transformer:
The main symptoms of short circuit fault of power transformer are serious heating and abnormal output voltage of secondary winding. Usually, the more short circuit points between turns in the coil, the greater the short circuit current, and the more serious the transformer heating. The simple method of detecting and judging whether the power transformer has short-circuit fault is to measure the no-load current.
The no-load current value of a transformer with a short-circuit fault will be much greater than 10% of the full-load current. When the short circuit is serious, the transformer in the no-load power within a few seconds will quickly heat, touch the iron core will have a hot feeling. At this time without measuring the no-load current can be determined that the transformer has a short circuit point.
What is the difference between switching power supply and transformer in use?
Switching power supply: Switching power supply can be very stable to a certain range of voltage into a very precise low or high voltage (for example, 110V-250 input, output voltage can be stable control in the required voltage plus or minus 0.5V).
Transformer: the output voltage of the transformer is constantly changing with the input voltage, that is, the input voltage increases the output voltage also increases, the input voltage reduces the output voltage also decreases.
To sum up, it can be concluded that the switching power supply is the first AC into DC, DC through the power switch tube and then into a higher frequency AC voltage conversion through a high frequency transformer not only improve the efficiency and greatly reduce the volume after the high frequency, but also save the loss of copper and iron. Because it is controlled by the power switch tube, the time of the switch tube is short when the current is small, and the output voltage can be maintained. When the load is large, the switch tube keeps working to maintain the output voltage. Therefore, the output voltage of the switching power supply is stable, which can be used as a high precision instrument such as LED display screen.
In summary, the switching power supply is currently used in a more extensive range, more to meet the needs of the market, in the understanding of the difference between the above switching power supply and transformer, but also hope that the switching power supply manufacturers can do a good job of quality, do not damage the interests of customers because of the pursuit of interests.
Switching power transformer is a power transformer that has joined the switching tube. In addition to the voltage conversion function of the ordinary transformer in the circuit, it also has the function of insulation isolation and power transmission. It is generally used in switching power supply and other occasions involving high-frequency circuits.
Function and classification of switching power transformers
The switching power transformer and the switch tube together form a self-excited (or other-excited) type blocking oscillator to convert the input DC voltage into a high frequency pulse voltage.
Play the role of energy transfer and conversion. In a flyback circuit, the transformer converts the electrical energy into a magnetic field that can be stored when the switch is on and released when the switch is off. In a forward circuit, when the switch tube is on, the input voltage is supplied directly to the load and the energy is stored in the inductor. When the switch tube ends, the energy storage inductor continues to transfer to the load.
Classification:
Switching power transformers are divided into single excitation switching power transformers and double excitation switching power transformers. The working principle and structure of the two kinds of switching power transformers are not the same. The input voltage of the single excitation switching power supply transformer is a single polar pulse, and it is also divided into positive and reverse voltage output; The input voltage of the dual-excitation switching power supply transformer is a bipolar pulse, which is generally a bipolar pulse voltage output.
Switching power transformer characteristic parameters
Voltage ratio: The ratio of the primary voltage to the secondary voltage of the transformer.
DC resistance: namely copper resistance.
Efficiency: namely output power/input power *100[%].
Insulation resistance: Insulation ability between the windings of a transformer and between the cores.
Resistance: The extent to which a transformer can withstand a specified voltage within 1 second or 1 minute.
Principle of switching power transformer
For switching power supply, the working principle of switching transformer is different from that of ordinary transformer. Ordinary transformer input AC voltage or current positive and negative half cycle waveform is symmetric, and the input voltage and current waveform is generally continuous, within a period, the average value of the input voltage and current is equal to 0, this is the basic characteristics of the working principle of ordinary transformer; And switch transformer are generally working in switch state, its input voltage or current is generally not sequential, but staccato, the input voltage or current within a period of mean value most of all not equal to zero, therefore, also known as pulse transformer, switch transformer it is a common transformer switch transformer with the biggest difference in terms of working principle.
Through the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control switch tube, the DC voltage after rectification for high frequency switch on, so that the high frequency current into the high frequency transformer primary side of the switching power supply, so that the transformer secondary side to produce inductive current, after rectification you can get the required voltage or multi-channel voltage.
Detecting details of switching power transformers
1, by observing the appearance of the transformer to check whether there is obvious abnormal phenomenon:
For example, whether the coil lead is broken or unsoldered, whether the insulation material has burnt marks, whether the iron core fastening screw is loose, whether the silicon steel sheet is corroded, whether the winding coil is exposed, etc.
2. Insulation test:
Use multimeter R&Times; 10K block respectively measure the core and primary, primary and secondary, core and secondary, electrostatic shielding layer and vent secondary, secondary between the windings of the resistance value, multimeter pointer should refer to the infinite position. Otherwise, the transformer insulation performance is poor.
3, coil on and off detection:
Place the multimeter in R&Times; 1. In the test, if the resistance value of a certain winding is infinite, it indicates that the winding has circuit breakability fault.
4, discrimination of primary and secondary coils:
The primary pin and secondary pin of the power transformer are generally led from both sides respectively, and the primary winding is marked with 220V, the secondary winding is marked with the rated voltage value, such as 15V, 24V, 35V, etc. They are identified by these markers.
5. Detection of no-load current:
A. In the direct measurement method, all the secondary windings are open circuit, and the multimeter is placed in the AC current stop (500mA), and the primary winding is connected in series. When the primary winding plugs into the 220V AC mains, the multimeter indicates the no-load current value.
This value should not be greater than 10% ~ 20% of the transformer's full load current. The normal no-load current of the power transformer for common electronic equipment should be about 100mA. If it exceeds too much, it indicates that the transformer has a short-circuit fault.
B. Indirect measurement method: a 10/5W resistance is connected in series in the primary winding of the transformer, and the secondary is still completely no-load. Turn the multimeter to ac. After the power is added, the voltage drop U at both ends of the resistor R is measured with two meter pens, and then the no-load current I empty is calculated by Ohm's law, that is, I empty =U/R. F? Detection of no-load voltage.
The primary power transformer is connected to 220V mains, and the no-load voltage value of each winding (U21, U22, U23, U24) is measured with a multimeter alternating voltage in turn. The allowable error range is generally: the high-voltage winding ≤±10%, the low-voltage winding ≤±5%, and the voltage difference between the two groups of symmetrical windings with the center tap should be ≤±2%.
6. Test the temperature range of the power transformer:
General small power transformer allowable temperature rise of 40℃ ~ 50℃, if the quality of insulating materials used is good, allowable temperature rise can also be improved.
7. Detect and discriminate the namesake end of each winding:
When using a power transformer, sometimes two or more secondary windings can be connected in series in order to obtain the required secondary voltage. When the power transformer is used in series, the namesake ends of the windings participating in series must be connected correctly and there can be no mistake. Otherwise, the transformer will not work properly.
8. Comprehensive detection and discrimination of short-circuit fault of power transformer:
The main symptoms of short circuit fault of power transformer are serious heating and abnormal output voltage of secondary winding. Usually, the more short circuit points between turns in the coil, the greater the short circuit current, and the more serious the transformer heating. The simple method of detecting and judging whether the power transformer has short-circuit fault is to measure the no-load current.
The no-load current value of a transformer with a short-circuit fault will be much greater than 10% of the full-load current. When the short circuit is serious, the transformer in the no-load power within a few seconds will quickly heat, touch the iron core will have a hot feeling. At this time without measuring the no-load current can be determined that the transformer has a short circuit point.
What is the difference between switching power supply and transformer in use?
Switching power supply: Switching power supply can be very stable to a certain range of voltage into a very precise low or high voltage (for example, 110V-250 input, output voltage can be stable control in the required voltage plus or minus 0.5V).
Transformer: the output voltage of the transformer is constantly changing with the input voltage, that is, the input voltage increases the output voltage also increases, the input voltage reduces the output voltage also decreases.
To sum up, it can be concluded that the switching power supply is the first AC into DC, DC through the power switch tube and then into a higher frequency AC voltage conversion through a high frequency transformer not only improve the efficiency and greatly reduce the volume after the high frequency, but also save the loss of copper and iron. Because it is controlled by the power switch tube, the time of the switch tube is short when the current is small, and the output voltage can be maintained. When the load is large, the switch tube keeps working to maintain the output voltage. Therefore, the output voltage of the switching power supply is stable, which can be used as a high precision instrument such as LED display screen.
In summary, the switching power supply is currently used in a more extensive range, more to meet the needs of the market, in the understanding of the difference between the above switching power supply and transformer, but also hope that the switching power supply manufacturers can do a good job of quality, do not damage the interests of customers because of the pursuit of interests.






.jpg)